In an era defined by interconnected devices and digital ecosystems, ensuring the integrity and trustworthiness of every connected device is paramount.
Device attestation solutions emerge as indispensable tools, providing a shield against unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious activities.
Cybersecurity and trustworthiness of IoT devices are becoming more and more vital for society, industry and organizations. Device attestation is a security control for assuring the integrity of IoT devices and the software they run.
This article explores the significance of Device Attestation as a Service, a streamlined solution that elevates the security posture of organizations without the burden of in-house complexities.
What is device attestation? Delving into the Concept of ‘Attestation’
What is device attestation? Moving deeper into the concept, when we refer to ‘attestation’, it implies the existence of a ‘secure environment’, commonly known as a Root of Trust (RoT). The RoT is responsible for securely storing and processing sensitive information, such as cryptographic keys, and ensuring the overall security of a device.
Identity Injection
Identity injection is a crucial process in information systems, seamlessly integrating identity information into various device components, providing evidence about a device's identity.
Device attestation is a security mechanism used to verify the integrity and authenticity of a device. It provides unique digital identities to devices, allowing them to authenticate themselves when required, helping to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches and malicious activity.
During attestation, various characteristics of the device, such as its hardware, firmware, and software, are examined to generate evidence of its trustworthiness. This evidence is often presented in the form of cryptographic certificates, signed by a trusted entity, and serves to assure that the device is genuine, secure, and has not been compromised.
Key Injection
Device attestation focuses on verifying the integrity and legitimacy of a device, whereas identity injection involves associating identity information with various components in a system. Key injection is specifically concerned with securely embedding cryptographic keys into devices or systems. This process plays a crucial role in enhancing both security and identity management.
Key injection refers to the process of securely embedding cryptographic keys into a device. Cryptographic keys are essential for various security functions, such as encryption, decryption, and digital signatures. A cryptographic digital signature serves a crucial role, allowing the relying party to ascertain the device's identity, its manufacturer, and the assurance that it has not been subject to unauthorized alterations prior to its connection to the network.
Key injection is typically performed during the manufacturing or provisioning phase of a device's lifecycle. In the context of device attestation, key injection is tied to the generation and protection of cryptographic keys within a device's Root of Trust (RoT). The RoT, being a secure and tamper-resistant component, is responsible for storing and managing the keys used in the attestation process. These keys play a crucial role for credentialing and authenticating devices.
When is device attestation required?
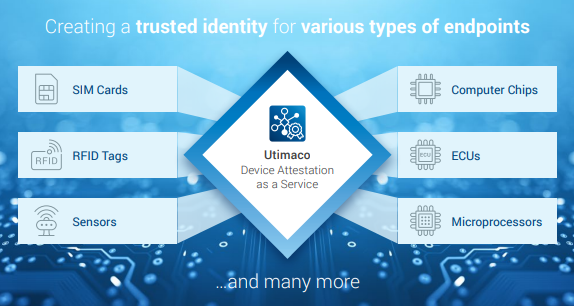
Device attestation is generally required in scenarios where it is essential to establish the trustworthiness and integrity of a device before allowing it access to certain resources or services. Depending on the particular requirements of the system or application, there may be variations in the processes and circumstances required for device attestation. Some examples are:
- Bootstrapping and Initial Configuration:
Device attestation may be required during the initial setup of a device, particularly in enterprise or IoT environments, to ensure that the device is authentic and has not been tampered with during manufacturing or shipping.
- Access Control and Authorization
Systems may require device attestation before permitting access to networks, services, or sensitive data in order to verify that the connecting device is authentic and compliant with security policies. This frequently entails verifying the software and configuration of the device are unmodified.
- Secure Communication and Data Exchange
Device attestation can be used in scenarios in which secure communication is essential, including financial transactions or the sharing of sensitive data, to make sure that both communicating devices are trustworthy and uncompromised.
- Cloud Services and Remote Access:
Attestation processes are used to verify the identity and security status of devices when connecting to cloud services or attempting to access them remotely. This helps prevent unauthorized access.
- IoT Security
To ensure that only authorized and secure devices are a part of the network, device attestation is essential in the context of the Internet of Things. This helps prevent malicious devices from compromising the integrity of the entire IoT ecosystem.
- Payment Transactions
In the context of payment transactions, device attestation plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of the devices involved in the transaction process. Some examples include:
- Device Identity Verification: In financial transactions conducted through electronic devices, device attestation ensures the security of the transaction by verifying the legitimacy of the device initiating or participating in a payment transaction
- Security Point-of-Sale (POS) Devices: Before allowing a device to initiate a payment transaction, the payment system may require device attestation to confirm that the device meets specific security standards and has not been tampered with.
- Protecting Sensitive Information: By ensuring that the device processing the transaction is secure and has not been compromised, device attestation assists in protecting sensitive financial information. This is particularly important when payment credentials such as credit card information or authentication tokens are at risk.
- Protection of Critical Infrastructure
For the protection of critical infrastructure, where connected devices' integrity, security, and reliability are vital, device attestation is essential. Examples include:
- Access Control: Ensures only authorized, trustworthy devices access critical infrastructure, preventing security threats.
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: Blocks unauthorized devices and safeguards against tampering to maintain system integrity.
- Smart Grid Integrity: Verifies device integrity in smart grids for reliable and secure electricity generation and distribution.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communications: Device attestation is used in automotive systems where vehicles communicate with infrastructure (V2I) or with each other (V2V) to verify the security and legitimacy of the communicating entities, preventing malicious tampering.
- Securing Networks: Guards communication networks within critical infrastructure against unauthorized devices and cyber attacks.
- Emergency Response Systems: Ensures secure communication devices for reliable operations in public safety and healthcare.
- Protection Against Insider Threats: Mitigates insider threats by allowing only authorized devices without compromise.
Implementing Device Attestation
Implementing device attestation can be done through various methods, and choosing between implementing it as a service or on-premises depends on specific use cases, resource availability, and organizational preferences.
Opting for an on-premise solution comes with inherent challenges. Custom development requires significant resources, including time, effort, and expertise, leading to potential delays and higher development costs. Additionally, managing an on-premise solution entails the responsibility of maintaining infrastructure, ensuring security updates, as well as the requirement to address any unforeseen issues. All of these can place a strain on any organizational structure.
Contrastingly, adopting Device Attestation as a Service offers numerous advantages. Cloud-based services provide a cost-effective and scalable solution, eliminating the need for substantial upfront investments in infrastructure. The managed nature of these services means that organizations can benefit from expert maintenance, updates, and security measures without the operational overhead. With global accessibility and the ability to leverage specialized security expertise, implementing device attestation as a service ensures a streamlined and efficient approach to securing devices in diverse and dynamic environments.
Unlocking Secure Connectivity: Device Attestation as a Service
Device Attestation as a Service takes the complexity out of assigning identities and validating device authenticity and integrity. By outsourcing these critical functions to trusted solution providers, organizations can seamlessly integrate robust security measures without the need for internal expertise or infrastructure. It also allows for a centralized and standardized approach to device trust, making it easier to enforce security policies across a diverse set of devices.
For organizations involved in manufacturing devices or components, the security of each device is paramount. Device Attestation as a Service streamlines this process by tapping into the expertise and resources of external providers, ensuring a robust security framework without extensive internal investments.
Numerous advantages of Device Attestation as a Service contribute to enhanced security, streamlined processes, and efficient management of connected devices. The following detail certain use cases and key advantages:
Enhanced Security
- Trustworthiness Verification: Device attestation as a service verifies the authenticity and integrity of connected devices, ensuring they meet predefined security standards before accessing networks or services.
- Protection Against Unauthorized Access: The service helps to prevent unauthorized access by verifying the authenticity of devices, which decreases the risk of malicious activity and data breaches.
Manufactured Device Security
- Effective Security Measures: The service provides a productive means of ensuring the security of every device for organizations involved in the manufacturing process. It leverages external resources to fortify security without requiring extensive internal investments.
Scalability
- Adaptability to Growth: The service's scalability enables organizations to modify and expand their security measures in response to evolving requirements and the growing number of connected devices.
Outsourcing Complexity
- Streamlined Processes: The service outsources the complex tasks of assigning identities and validating device authenticity and integrity to trusted solution providers. This makes it easier to deploy security measures, especially for organizations with lack of internal resources.
Reduced Operational Disruptions
- Swift Implementation: Security measure implementation is made quick and efficient with the help of device attestation as a service. This ensures that security protocols are followed without disrupting ongoing operations, thereby facilitating a seamless integration process.
Flexibility & Accessibility - Cloud-based versus On-premise
- Cloud-based: Cloud solutions provide flexibility, allowing users to access resources from anywhere with an internet connection. This is advantageous for organizations with remote or distributed teams.
- On-premise: On-premise solutions may require physical presence at the location where the infrastructure is set up, limiting accessibility and flexibility.
Collaborative and Remote Work
- In a world where remote work is prevalent, organizations benefit from cloud-based collaboration tools when utilizing a cloud-based Device Attestation as a Service solution. These solutions facilitate seamless communication, file sharing, and project collaboration, enabling teams to work efficiently from various locations.
Cost-effective Solution
- Resource Optimization: Outsourcing device attestation processes can lead to cost savings by optimizing resource allocation. Organizations can focus on their core competencies while relying on specialized providers for security-related tasks.
- Central and Remote Key Management in One Platform.
Device Attestation: A Secure Future for Connected IoT Devices
As the number of connected devices continues to grow, scalability becomes a vital consideration. Device Attestation as a Service is inherently scalable, empowering organizations to adapt to changing needs and seamlessly accommodate the increasing complexity of their connected ecosystems. This adaptability positions organizations with a strategic advantage in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity risks.
In embracing a cloud-based device attestation service, organizations unlock a future where security is not just a necessity but an efficient, outsourced solution. This transformative approach not only strengthens organizations against current threats but also prepares them to meet the dynamic challenges of tomorrow's interconnected world.
For further information, download Utimaco’s Device Attestation as a Service brochure.