Welcome to a new era of data governance in the European Union as the European Data Act takes center stage, marking a pivotal moment in shaping a fair and innovative data economy.
With its recent entry into force, this landmark legislation sets out a comprehensive framework defining rights to access and utilize data generated within the EU, spanning across diverse economic sectors.
At its core, the European Data Act aims to streamline data sharing, particularly emphasizing the facilitation of industrial data exchange. Let's delve deeper into the implications of this transformative legislation and its potential to reshape the landscape of data management and security within the EU.
The EU Data Act entered into force on 11 January 2024, and it will become applicable in September 2025.
What is the EU Data Act?
The EU Data Act is a legislative proposal aimed at modernizing and harmonizing data governance across the European Union (EU). It seeks to establish rules and standards for data sharing and data access, particularly in sectors like healthcare, research, and public administration. The act aims to promote data-driven innovation while safeguarding privacy and security concerns.
EU Data Act: Shaping the Future of Europe's Digital Transformation
The journey towards a more equitable and innovative digital landscape in Europe reached a significant milestone on 23 February 2022, with the European Commission's proposal of the European Data Act. This pivotal legislation, aimed at fostering fairness in the digital realm and driving forward innovation, culminated in a political agreement between the European Parliament and the Council on 28 June 2023.
Integral to the Commission's broader data strategy, the Data Act stands as a cornerstone in achieving the ambitious objectives set for the 2030 Digital decade. Working in tandem with the Data Governance Act, which became applicable in September 2023, the EU Data Act establishes crucial processes and structures to facilitate data sharing among companies, individuals, and the public sector.
The EU Data Act operates in conjunction with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), reinforcing and complementing its principles and provisions. While the GDPR primarily focuses on personal data protection and privacy rights, the Data Act extends its scope to encompass various types of data beyond personal data. However, both regulations share common objectives of enhancing data transparency, ensuring data security, and empowering individuals with greater control over their data.
What are the Benefits of the EU Data Act?
The Data Act will remove barriers to data access for both private and public sector organizations, while maintaining incentives to invest in data generation by ensuring a balanced control over the data for those who create it.
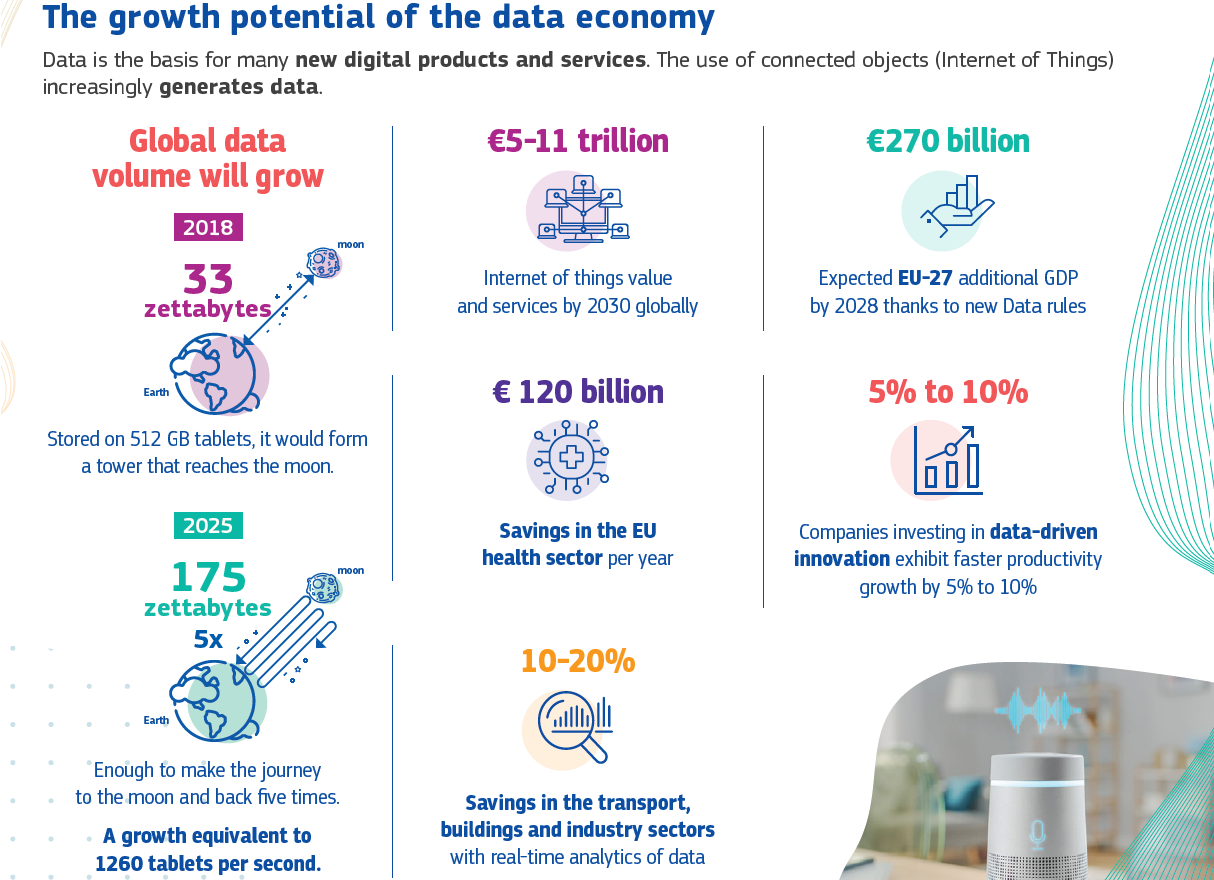
Source: European Commission - Data Act Factsheet
The EU Data Act introduces a series of measures designed to address key challenges and opportunities in the digital landscape:
- Enhanced Data Security & Accessibility: Users of connected devices gain the right to access data generated by these devices and related services. This empowers users to share such data with third parties, fostering aftermarket services and driving innovation. Meanwhile, manufacturers are incentivized to invest in quality data generation, safeguarding their trade secrets
- Protection from Unfair Contractual Terms: The Act includes provisions to shield EU companies from unfair contractual terms unilaterally imposed upon them. These measures promote fair negotiations, enabling SMEs to confidently engage in the digital marketplace
- Emergency Access to Private Sector Data: Public sector bodies are granted mechanisms to access and utilize private sector-held data during emergencies such as floods or wildfires. This ensures improved emergency response and effective implementation of legal mandates when required data is not readily accessible through other means
- Increased Consumer Choice and Competition: Customers gain the freedom to switch between different cloud data-processing service providers, fostering competition and choice while mitigating vendor lock-in risks. Additionally, the Act implements safeguards against unlawful data transfers, ensuring a reliable and secure data-processing environment
- Promotion of Interoperability Standards: The Act promotes the development of interoperability standards for data-sharing and processing, aligning with the EU Standardisation Strategy to facilitate seamless data exchange and processing across platforms and systems.
Overall, the EU Data Act aims to create a more transparent, fair, and secure digital environment that benefits both individuals and businesses, while also fostering innovation and economic growth within the European Union.
Who is influenced by the EU Data Act?
The EU Data Act affects a wide range of stakeholders both inside and outside the European Union. Important parties impacted by the EU Data Act consist of:
- Organizations and Corporations: All types of businesses are affected by the Data Act, including small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and multinational corporations. They have to abide by the Act's rules about the collection, use, and handling of data. This has an impact on a variety of industries, including manufacturing, technology, healthcare, banking and financial services.
- Customers and Individuals: As required by the Data Act, individuals gain more control and transparency over their personal data. They have the right to access and share data generated by connected devices, ensuring greater privacy protection and empowering them to make informed decisions about their data usage.
- Government Agencies and the Public Sector: The Data Act improves public sector organizations' capacity to provide services, respond to emergencies, and carry out regulatory mandates by granting access to private sector-held data for specific purposes, including emergencies.
- Technology Service Providers: Cloud service providers, data processors, and other technology companies are influenced by the Data Act's provisions, particularly those related to data portability, interoperability, and security. They must adhere to standards and requirements set forth in the Act to ensure compliance and maintain consumer trust.
- Regulatory Authorities and Data Protection Agencies: The EU's regulatory bodies and data protection agencies are responsible for enforcing the Data Act's provisions. They play a crucial role in monitoring compliance, investigating potential violations, and imposing penalties on non-compliant entities.
- Third-country and International Partners: International partners and third countries who seek to share data with EU entities may be impacted by the Data Act's rules on data transfers and cross-border data flows. Businesses that operate internationally may need to adhere to EU data protection standards.
- Research Institutions and Academia: Organizations engaged in research and academia may benefit from the Data Act's provisions, particularly those related to data access and sharing. The Act promotes collaboration and knowledge exchange while ensuring data security and privacy.
- Restrictions for Gatekeepers: Gatekeepers are unable to capitalize on the new user right to share data with third parties. This means they are prohibited from both sharing data themselves and receiving data from users, as making data available to designated gatekeepers is strictly prohibited.
Overall, the EU Data Act has a wide-ranging impact on various sectors and stakeholders, shaping the digital landscape, encouraging data-driven innovation, and protecting individuals' privacy rights in the European Union and beyond.
How is Data defined under the scope of the EU Data Act?
The data under the scope of the EU Data Act encompasses a wide range of information generated and processed within the European Union. This includes:
- Personal & Non-personal Data: Data that is collected through in-scope products or during providing in-scope products. This includes raw data generated by the user interface and device, but excludes information inferred or derived from such data.
- Connected Device Data: Metrics from IoT devices and sensors.
- Industrial Data: Metrics from manufacturing processes and machinery.
- Cloud Data: Information stored and processed through cloud services.
- Public Sector Data: Datasets held by government agencies.
- Emergency Data: Information accessed during crises for emergency response.
These categories reflect the Act's aim to ensure transparency, privacy, and innovation in data handling.
The EU Data Act - How does it impact your Data Security Strategy?
The EU Data Act emphasizes the imperative of protecting sensitive data, prioritizing security as paramount in the digital landscape. The Act mandates stringent data protection measures and requires businesses to maintain strong security protocols to protect commercially sensitive information, trade secrets, and data subject to intellectual property rights or confidentiality obligations under European law.
Paragraph 8 of the EU Data Act details,
“The principles of data minimization and data protection by design and by default are essential when processing involves significant risks to the fundamental rights of individuals. Taking into account the state of the art, all parties to data sharing, including where within scope of this Regulation, should implement technical and organisational measures to protect these rights. Such measures include not only pseudonymization and encryption, but also the use of increasingly available technology that permits algorithms to be brought to the data and allow valuable insights to be derived without the transmission between parties or unnecessary copying of the raw or structured data themselves”.
Emphasizing the importance of compliance with the European regulatory framework, the Act ensures that data processing service providers adopt comprehensive technical, legal, and organizational safeguards to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and conflicts with EU or national laws, aligning closely with the principles outlined in paragraph 8 above. By prioritizing the protection of sensitive data, the EU Data Act aims to bolster trust, foster innovation, and uphold privacy rights within the digital ecosystem, thereby reinforcing its commitment to safeguarding individuals’ fundamental rights in the digital age.
The time to prepare for the EU Data Act is now! Complying with the new rules on data transfer provision and use is crucial to safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access. With LAN Crypt File and Folder Encryption, your sensitive data will be securely encrypted at Rest and in Motion, accessible only to authorized users.






