Navigating the quantum leap in the cybersecurity domain demands a proactive and agile approach towards quantum-resistant cryptography. In this thought-provoking piece, we'll explore the imminent quantum threat, assess the current state of post-quantum algorithms, and reveal practical strategies that leaders in the digital security sector can employ to safeguard their data from the quantum storm on the horizon.
Understanding the Quantum Threat – Are you PQC-ready?
The race toward quantum computing power is accelerating, and with recent breakthroughs from pioneering companies, we are closer than many realize to the era of quantum supremacy: just recently, Microsoft and Quantinuum moved one step closer to a commercial quantum computer. They improved the logical error rate of their supercomputer by 800 times by creating an innovative qubit virtualization system in ion-trap hardware, resulting in four highly reliable logical qubits from only 30 physical qubits.
This imminent milestone will render standard asymmetric cryptography, such as RSA and ECC, vulnerable to decryption.
The Present State of Encryption Vulnerability – Quantum-powered Cyber Attacks
Current-day encryption methodologies stand as a thin barrier against the computational prowess of future quantum computers. Algorithms that take thousands of years to break with classical computing could be dismantled in a matter of hours by quantum machines. This disparity in cryptographic resilience is the heart of the quantum threat that cybersecurity professionals must address. Although quantum computers are not yet available, they do have an impact on today's cryptographic applications – represented by two attack types:
1. Store now, decrypt later
Attackers could obtain sensitive information now and wait until quantum computers are available to decrypt it. This is especially relevant if your organization handles sensitive information with a long confidentiality span.
2. Digital signatures can be broken
By “computing” credentials from public information, an attacker could approve requests or sign documents impersonating someone else. This can also happen retroactively in the future with older signatures if they are not updated.
One cannot say with certainty when a quantum computer will be available that can crack standard crypto such as RSA. However, there are various hypotheses that range from 2030 to 2035.
RSA-2048 is only considered secure until 2030.
(according to NIST SP 800-78-5)
You may be thinking, "2030 is a few years away; why should I worry about it now? Planning your Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC) migration now is essential to ensure the long-term security of your data and applications for three main reasons:
- Although the first sufficient quantum computers are expected in 2030, it cannot be ruled out that they will not be available earlier.
- Crypto discovery and migration will take time.
- Legacy code and libraries will be around for a long time.
Basically, you are left with two options:
1. Plan your PQC Migration now.
2. Do nothing and risk data security. (There’s a great chance your future self will not thank you for this decision.)
The good news: The development and standardization of PQC is also progressing.
Start by evaluating your post quantum cryptography options and plan your migration with Utimaco.
Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC): A Strategic Imperative
Let’s dissect the current landscape of PQC and the critical role it holds in data protection against quantum adversaries.
Navigating NIST Standards and the CNSA Suite 2.0
NIST – the National Institute of Standards and Technology – recognized the potential threat of quantum computing as early as 2016. As a result, they have launched a standardization process to establish standards for algorithms that are resistant to quantum computers. This initiative is recognized worldwide by many institutions that welcome it.
To date, NIST has defined four algorithms to be standardized:
- CRYSTALS-Kyber (ML-KEM)
- CRYSTALS-Dilithium (ML-DSA)
- FALCON
- SPHINCS+ (SLH-DSA)
Other algorithms have advanced to the fourth round of the standardization process, the results of which are expected to be announced later this year. In addition to the NIST process, there are other reputable institutions that define quantum-resistant algorithm suites or recommendations, such as the Commercial National Security Algorithm (CNSA) Suite 2.0 shown here:
For Software and firmware signing:
- LMS
- XMSS
For General public key algorithms for quantum resilience:
- Key establishment: CRYSTALS-Kyber (ML-KEM)
- Digital Signatures: CRYSTALS-Dilithium (ML-DSA)
For Symmetric key algorithms:
- AES
- SHA
Overview – Your choice of PQC algorithms
| Algorithm | Method | Status | |
| Encryption / Key Encapsulation | CRYSTALS-Kyber | Lattice-based | NIST Draft Standard published: FIPS 203 (ML-KEM) |
| Classic McEliece | Code-based | NIST PQC Standardization Round 4 | |
| Bike | Code-based | NIST PQC Standardization Round 4 | |
| HQC | Code-based | NIST PQC Standardization Round 4 | |
| Frodo-KEM | Lattice-based | Recommended by BSI (German Federal Office for Information Security) | |
| Digital Signatures | CRYSTALS-Dilithium | Lattice-based | NIST Draft Standard published: FIPS 204 (ML-DSA) |
| SPHINCS+ | Hash-based | NIST Draft Standard published: FIPS 205 (SLH-DSA) | |
| FALCON | Lattice-based | NIST Selected Algorithm to be standardized | |
| LMS / HSS | Stateful Hash-based | Recommended by NIST (apart from standardization process) | |
| XMSS / XMSS-MT | Stateful Hash-based | Recommended by NIST (apart from standardization process) |
The PQC Implementation Paralysis
Many organizations face a PQC implementation paradox. The hesitation to transition to PQC could leave digital assets vulnerable, yet adopting unproven cryptographic frameworks invites operational and security risks in equal measure.
This uncertainty is further exacerbated by the fact that there is no silver bullet. You cannot assume that the algorithms from the list will be a 1:1 replacement. You need to consider which cryptographic use cases your organization has and test which PQC algorithm fulfills this use case in your environment.
Crafting a PQC Migration Strategy for quantum resilience
A robust quantum-resilient strategy encompasses more than just upgrading cryptographic algorithms. It involves a holistic approach to secure data against potential quantum threats, encompassing technology, policy, and organizational readiness.
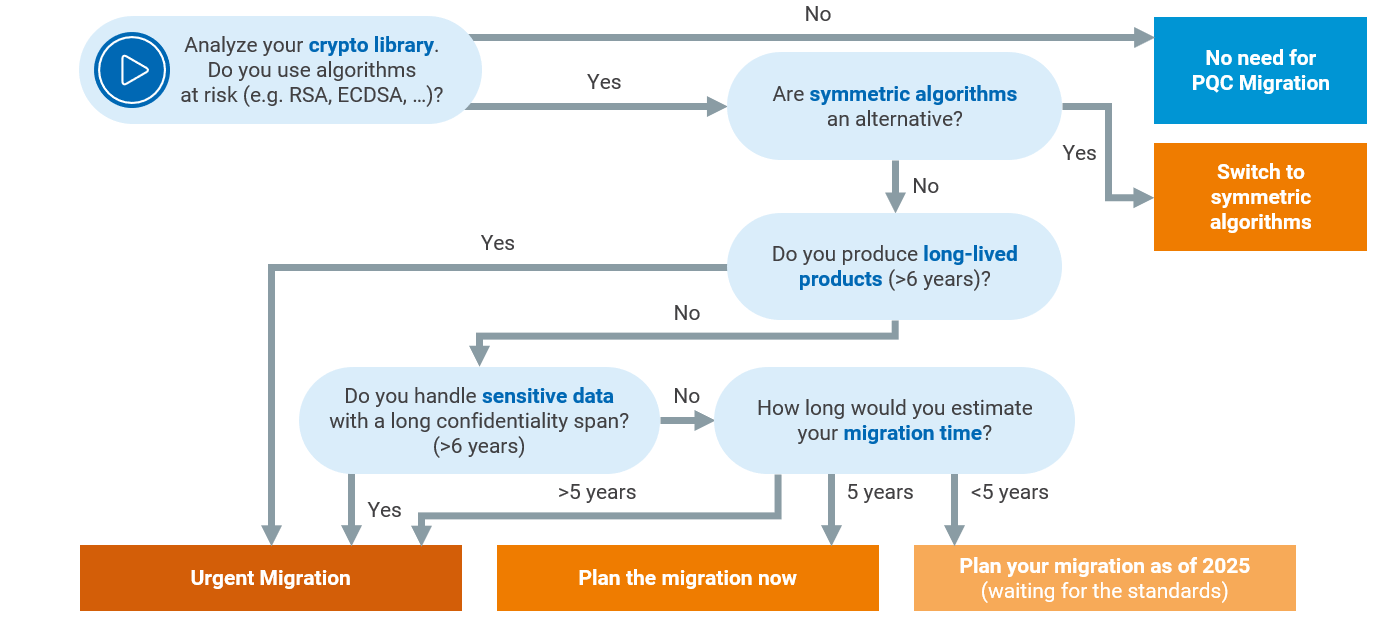
Examining successful PQC migration efforts illuminates the path forward for organizations. By deploying a hybrid approach that incorporates PQC alongside classical algorithms, companies are preparing for the quantum age without sacrificing their current security postures.
The role of Crypto Agility and HSMs
“The most important approach is to be flexible; the use of implementations and applications that can most easily be adapted to the cryptographic security offerings and a plan for transitioning to them offer the best solution.” – NIST SP 800-57
Crypto agility applies not only to your application, but also to the devices you use. When upgrading cryptographic applications and encryption keys for the post-quantum era, hardware security modules (HSMs) play a critical role. The HSM is an essential element of your cryptographic infrastructure because it is the trust anchor for your cryptographic keys and performs cryptographic processes based on algorithms and for key generation, management, and storage.
Crypto-agile HSM solutions are designed to accommodate the swift integration of PQC algorithms, offering a layer of flexibility that is indispensable to long-term cybersecurity planning.
Thus, when choosing an HSM vendor, crypto agility is a critical factor.
What's Next? Preparing for the Inevitable Quantum Era
The quantum era is not just a technological milestone—it is a security watershed that will redefine the landscape for decades to come. Now is the time to engage in post quantum cryptography, to ensure that as the quantum horizons expand, our data remains secure.
Quantum Computing and the Velocity of Change
The pace at which quantum computing is evolving underscores the imperative for immediate action. Waiting for a clear and present danger before adopting PQC is akin to playing the odds with increasingly outdated cryptographic protocols.
The Long-Term Benefits of Proactive Quantum Resilience
Organizations that proactively invest in quantum-resilient cryptography stand to gain more than just secure data transmissions. They pave the way for technological innovation, operational excellence, and a reputation for being at the vanguard of digital security.
Partnering with PQC Innovators
At Utimaco, we're proud to be at the forefront of research and innovation in the field of Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC). As quantum computing evolves, so must cryptography.
Our experts participate in several influential committees dedicated to shaping the future of PQC, such as:
- NIST PQC Consortium, PQC Consortium: Work Streams Interoperability, Discovery
- X9 Post Quantum Cryptography Committee
- ETSI Quantum-Safe Cryptography (QSC) Working Group
- PQC Consortium: PQC Workstream
- And several more
These committees serve as hubs for collaboration, knowledge sharing, and driving standards that will define the next generation of cryptographic protocols.
In conclusion, quantum computing poses unprecedented challenges to the field of cryptography. However, by taking a proactive, informed, and collaborative approach, we can turn these challenges into opportunities to enhance our data security. The time for post-quantum cryptography is not in some far-off quantum future—it is now.
Utimaco’s Hardware Security Modules – PQC-ready by design
Utimaco’s General Purpose HSMs are designed crypto-agile and can be in-field upgraded with PQC algorithms such as CRYSTALS-Kyber, CRYSTALS-Dilithium, LMS/HSS, and XMSS/XMSS-MT. We also follow the standards and continuously develop our solutions. As a result, we have successfully completed several PQC migration and implementation projects with various customers.
The best part: You can test PQC algorithms in your infrastructure with our Q-safe simulator.
Explore Utimaco PQC solutions at RSA Conference 2024!
Are you planning to attend RSA Conference 2024? Don't miss the opportunity to hear our experts live! Utimaco’s CTO, Nils Gerhardt, will reveal strategies for future-proofing your digital infrastructure against the inevitable quantum revolution. Catch him at the Briefing Center on Wednesday, May 8, 2024, from 11:10 AM to 11:30 AM PT, or visit our booth 5256 for further insights.
Additionally, ensure you don't miss out on the exclusive on-demand session available at RSA - "PQC in Practice – Use Cases, Migration Tips, and a Free Demo Tool." Join our experts as they share first-hand experiences from successful PQC migration projects.

Furthermore, stop by our booth 5256 to experience a live PQC Demo firsthand. For more details about our presence at RSA 2024, including additional sessions and booth activities, please visit here.
About the Author
Lena Backes is an IT Marketing expert with more than 10 years of experience working in the B2B sector. In her professional career, she has gained extensive knowledge in various areas, including cybersecurity, network management, enterprise streaming, and software asset management. In her current role she is responsible for product positioning of Utimaco’s cybersecurity products and solutions, with a particular focus on data protection, blockchain technology, and post quantum cryptography.






