Building Trust across the eHealth environment
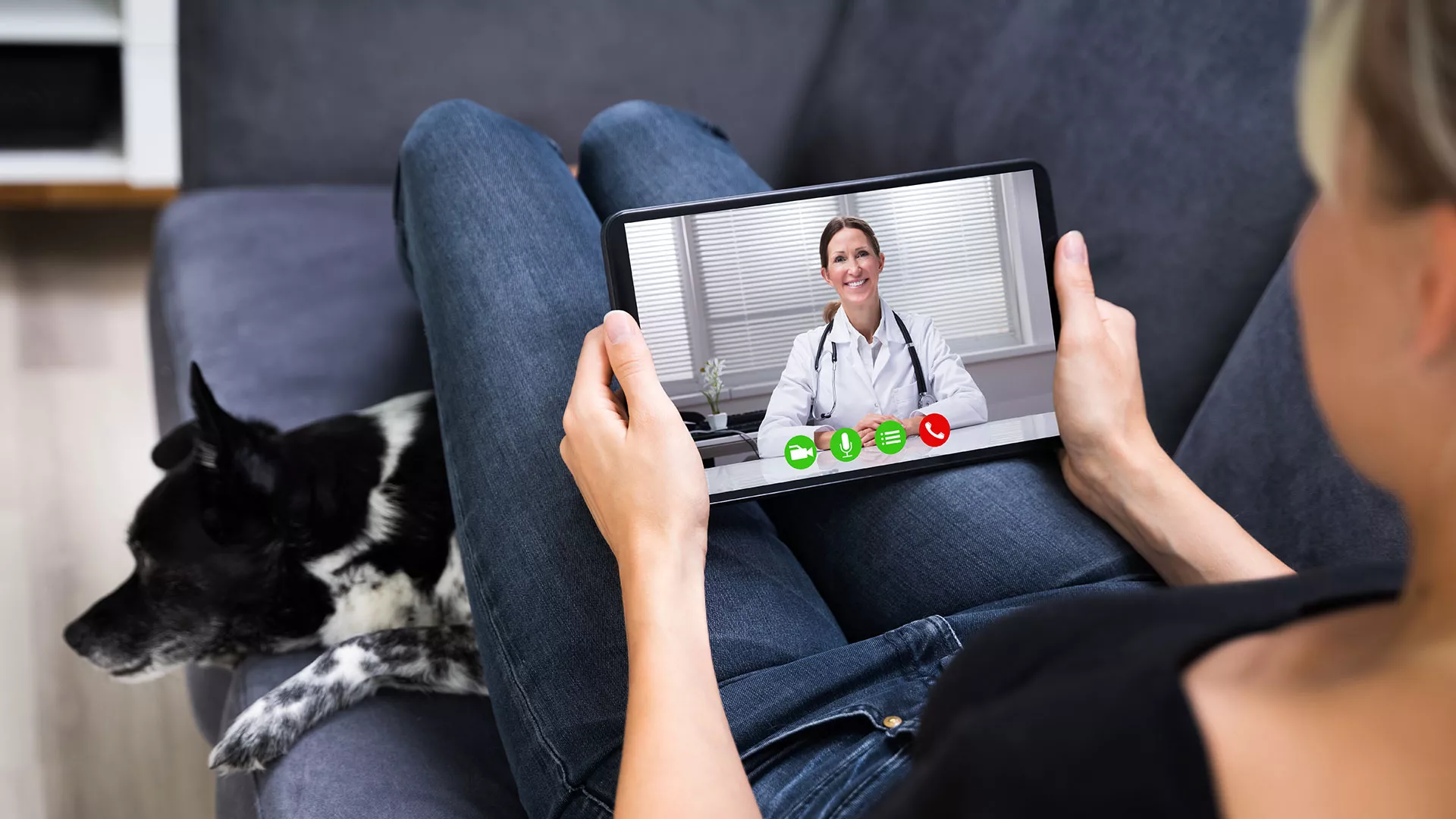
Digital transformation in healthcare has led to innovations such as telemedicine and remote patient monitoring.
Ensuring that the connected environments across hospitals, doctor’s surgeries, medical insurance companies, and further stakeholders are securely protected, is just as important as protecting the patient data itself. Healthcare providers are now forced to rethink their approach in ensuring that generation, storage and sharing of patient data is met with adequate security.
While curing disease and saving lives is the main objective of health care, one of its greatest vulnerabilities is device and data security as well as data privacy - and this remains susceptible to cyber-attack.
eHealth is a broad term covering a great deal of territory and can range from digital patient authentication via health insurance cards, data generation and transmission of smart diagnostic devices to regional systems where patients can access online data through national eHealth application schemes for the purpose of accessing medical records, booking appointments, including ePrescription services. At times, services extend to cross border eHealth information sharing.
As data is generated, shared, and managed by a variety of parties; identity and access management for the connected environments as well as data protection are key attributes across the eHealth infrastructure.
The requirement is not only to ensure that patient data is generated, recorded, processed, and transferred across devices, platforms, and processes in a highly secure way, but also in compliance with legal and user consent.